Hacking Germany’s Official Statistics with datenguideR
Lisa Hehnke
@DataPlanes
Fabio Votta
@favstats
Vroni Grupp
@vgeodata
Slides available at:
dg-berlinR.netlify.com
2020-02-05
What's ahead?
Introduction to the datenguideR infrastructure
Main functions of datenguideR and examples (
dg_call)Plotting function (
dg_map)Hackathon!
What's ahead?
Introduction to the datenguideR infrastructure
Main functions of datenguideR and examples (
dg_call)Plotting function (
dg_map)Hackathon!

How to datenguideR
First install datenguideR from GitHub (not yet on CRAN)

devtools::install_github("CorrelAid/datenguideR")How to datenguideR
First install datenguideR from GitHub (not yet on CRAN)

devtools::install_github("CorrelAid/datenguideR")
Admiral Ackbar says

How to datenguideR
First install datenguideR from GitHub (not yet on CRAN)

devtools::install_github("CorrelAid/datenguideR")
How to datenguideR
Functions start with dg_*

How to datenguideR
Functions start with dg_*

The rOpenSci Package guide states that:
Functions and arguments naming should be chosen to work together to form a common, logical programming API that is easy to read, and auto-complete.
This object_verb scheme:
- helps avoid namespace conflicts with packages that may have similar verbs
- makes code readable and easy to auto-complete
How to datenguideR
Functions start with dg_*

The rOpenSci Package guide states that:
Functions and arguments naming should be chosen to work together to form a common, logical programming API that is easy to read, and auto-complete.
This object_verb scheme:
- helps avoid namespace conflicts with packages that may have similar verbs
- makes code readable and easy to auto-complete
In the following we will learn about:
dg_descriptions: Meta datadg_search: Search Meta datadg_call: Make API Callsdg_map: Plot Maps
Metadata with dg_descriptions
Get all available meta data on statistics, substatistics, and parameters:
datenguideR::dg_descriptions## # A tibble: 3,419 x 11## stat_name stat_description stat_descriptio… substat_name## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> ## 1 AENW01 Entsorgte/behan… "**Entsorgte/be… <NA> ## 2 AENW02 Abgelagerte Abf… "**Abgelagerte … <NA> ## 3 AENW03 Entsorg.u.Behan… "**Entsorg.u.Be… <NA> ## 4 AENW04 Entsorgte/behan… "**Entsorgte/be… <NA> ## 5 AENW05 Abgelagerte Abf… "**Abgelagerte … <NA> ## 6 AENW06 Entsorg.u.Behan… "**Entsorg.u.Be… <NA> ## 7 AEW001 Entsorgungs- un… "**Entsorgungs-… <NA> ## 8 AEW001 Entsorgungs- un… "**Entsorgungs-… EBANL1 ## 9 AEW001 Entsorgungs- un… "**Entsorgungs-… EBANL1 ## 10 AEW001 Entsorgungs- un… "**Entsorgungs-… EBANL1 ## # … with 3,409 more rows, and 7 more variables: substat_description <chr>,## # param_name <chr>, param_description <chr>, stat_description_en <chr>,## # stat_description_full_en <chr>, substat_description_en <chr>,## # param_description_en <chr>Metadata with dg_descriptions
Variables are hierarchically organized on three levels: stat, substat and param. A stat may or may not have any substats and a substat may or not have any params. It completely depends on the variable.
stat level ¦--stat_name ¦--stat_description ¦--stat_description_en ¦--stat_description_full ¦--stat_description_full_en ¦ °--substat level ¦--substat_name ¦--substat_description ¦--substat_description_en ¦ °--param level ¦--param_name ¦--param_description ¦--param_description_enConfused?

Let's consider an example
Metadata with dg_descriptions
Let's consider the example of statistics on new German citizens (BEV008)
stat level ¦--stat_name ¦--stat_description ¦--stat_description_en ¦--stat_description_full ¦--stat_description_full_en ¦ °--substat level ¦--substat_name ¦--substat_description ¦--substat_description_en ¦ °--param level ¦--param_name ¦--param_description ¦--param_description_enMetadata with dg_descriptions
Let's consider the example of statistics on new German citizens (BEV008)
stat level ¦--stat_name: BEV008 ¦--stat_description: Einbürgerungen von Ausländern ¦--stat_description_en: Naturalizations of Foreigners ¦--stat_description_full: ... ¦--stat_description_full_en: ... ¦ °--substat level ¦--substat_name: STAKNW ¦--substat_description: Kontinente (einschl. staatenlos etc.) ¦--substat_description_en: Continents (Including Stateless Etc.) ¦ °--param level ¦--param_name: ST997 ¦--param_description: Staatenlos, unbekannt, ungeklärt, ohne Angabe ¦--param_description_en: Stateless, Unknown, Unsettled, without InformationMetadata with dg_descriptions
First, there is the stat_* level.
stat level¦--stat_name: BEV008¦--stat_description: Einbürgerungen von Ausländern¦--stat_description_en: Naturalizations of Foreigners¦--stat_description_full: ...¦--stat_description_full_en: ... ¦ °--substat level ¦--substat_name: STAKNW ¦--substat_description: Kontinente (einschl. staatenlos etc.) ¦--substat_description_en: Continents (Including Stateless Etc.) ¦ °--param level ¦--param_name: ST997 ¦--param_description: Staatenlos, unbekannt, ungeklärt, ohne Angabe ¦--param_description_en: Stateless, Unknown, Unsettled, without InformationMetadata with dg_descriptions
The variable stat_description_full_en includes a long English description of a given statistic (written up in Markdown):
Metadata with dg_descriptions
The variable stat_description_full_en includes a long English description of a given statistic (written up in Markdown):
Naturalizations of foreigners from GENESIS statistics "Naturalization Statistics" 12511) Naturalizations of foreigners
Explanation for the following statistics: 12511 Naturalization statistics
Conceptual content: Naturalizations
Naturalizations are the total number of naturalizations of foreigners carried out by German authorities in Germany and abroad in the course of the reporting year. In the case of naturalization, a foreigner is granted German citizenship by handing in a certificate of naturalization. For this, an application must be made and the foreign person concerned must meet certain requirements. Naturalizations occur in the majority on the basis of the Citizenship Act (StAG), but also by other legal bases that mostly regulate old and reparation cases. The naturalization statistics report on naturalizations carried out in Germany and abroad by German authorities in the course of the reporting year according to their previous nationality, legal grounds for naturalization, length of stay in the federal territory, gender, age, marital status and according to continuing or discontinued citizenship. The regional proof of naturalization cases relates to the place of residence of the naturalized person at the time of naturalization. The data does not include the acquisition of German citizenship by the birth of children of foreign parents born in Germany (pursuant to Section 4 (3) StAG).
Conceptual content: foreigners
Foreigners are all persons who do not have German citizenship, ie are not German within the meaning of Article 116 (1) of the Basic Law (GG). Stateless persons and people with unresolved citizenships also belong to this group of people.
Metadata with dg_descriptions
Next, there is the substat_* level. In the example, the substatistic splits new statistics by continent of origin (STAKNW).
stat level ¦--stat_name: BEV008 ¦--stat_description: Einbürgerungen von Ausländern ¦--stat_description_en: Naturalizations of Foreigners ¦--stat_description_full: ... ¦--stat_description_full_en: ... ¦°--substat level ¦--substat_name: STAKNW ¦--substat_description: Kontinente (einschl. staatenlos etc.) ¦--substat_description_en: Continents (Including Stateless Etc.) ¦ °--param level ¦--param_name: ST997 ¦--param_description: Staatenlos, unbekannt, ungeklärt, ohne Angabe ¦--param_description_en: Stateless, Unknown, Unsettled, without InformationOther possible examples of a substat for BEV008 is the statistic split up by age groups (ALTX04) or Length of Stay (AUFDA1).
Metadata with dg_descriptions
Next, there is the param_* level. In the example, we use ST997 which queries new citizens who were "stateless" or have unknown origins.
stat level ¦--stat_name: BEV008 ¦--stat_description: Einbürgerungen von Ausländern ¦--stat_description_en: Naturalizations of Foreigners ¦--stat_description_full: ... ¦--stat_description_full_en: ... ¦ °--substat level ¦--substat_name: STAKNW ¦--substat_description: Kontinente (einschl. staatenlos etc.) ¦--substat_description_en: Continents (Including Stateless Etc.) ¦ °--param level ¦--param_name: ST997 ¦--param_description: Staatenlos, unbekannt, ungeklärt, ohne Angabe ¦--param_description_en: Stateless, Unknown, Unsettled, without InformationYou might be thinking:

Don't worry, that's why we build dg_search()
How to use dg_search
dg_search matches your string with any variable in dg_descriptions, returning only rows with those matches.
Looking for variables where the string "vote" appears somewhere in the documentation:
dg_search("vote")## # A tibble: 90 x 5## stat_name stat_descriptio… stat_descriptio… substat_descrip…## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> ## 1 AI0501 Second Vote Sha… "** CDU / CSU s… <NA> ## 2 AI0502 SPD Second Vote… "** SPD second … <NA> ## 3 AI0503 FDP Second Vote… "** Second vote… <NA> ## 4 AI0504 Second Vote Sha… "** GREEN secon… <NA> ## 5 AI0505 Second Vote Sha… "** Second vote… <NA> ## 6 AI0506 Voter Turnout, … "** Voter turno… <NA> ## 7 AI0601 CDU / CSU, Euro… "** CDU / CSU v… <NA> ## 8 AI0602 SPD Vote Share,… "** SPD vote sh… <NA> ## 9 AI0603 FDP Share of Vo… "** FDP vote sh… <NA> ## 10 AI0604 Share of Votes … "** GREEN share… <NA> ## # … with 80 more rows, and 1 more variable: param_description_en <chr>How to datenguideR
Get Region IDs of all available NUTS-1 regions with dg_regions:
datenguideR::dg_regions %>% dplyr::filter(level == "nuts1")dg_call

The main work horse of datenguideR
How to use dg_call
Main arguments of dg_call:
| arguments | description |
|---|---|
| region_id | The ID of a specific region |
| stat_name | Main statistic |
| substat_name | Sub-statistic |
| parameter | Parameter Defaults to all |
| year | Year(s) |
| nuts_nr | NUTS level |
| lau_nr | LAU level |
| full_descriptions | Full descriptions Defaults to FALSE |
How to use dg_call
dg_call(region_id = 11, # 11 is Berlin (see dg_regions) year = 2017, # Specify Year stat_name = "BEV008", # Stats on New Citizens substat_name = "STAKNW", # By Continent parameter = "GESAMT") # All categories summed| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
id <chr> | name <chr> | year <int> | STAKNW <chr> | value <int> | GENESIS_source <chr> | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | Berlin | 2017 | GESAMT | 6479 | Einbürgerungsstatistik |
How to use dg_call
dg_call(nuts_nr = 1, # NUTS-1 year = 2017, # Specify Year stat_name = "BEV008", # Stats on New Citizens substat_name = "STAKNW", # By Continent parameter = "GESAMT") # All categories summed| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
id <chr> | year <int> | STAKNW <chr> | value <int> | name <chr> | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 2017 | GESAMT | 1188 | Saarland | |
| 11 | 2017 | GESAMT | 6479 | Berlin | |
| 12 | 2017 | GESAMT | 765 | Brandenburg | |
| 13 | 2017 | GESAMT | 526 | Mecklenburg-Vorpommern | |
| 14 | 2017 | GESAMT | 1560 | Sachsen | |
| 15 | 2017 | GESAMT | 734 | Sachsen-Anhalt | |
| 16 | 2017 | GESAMT | 701 | Thüringen | |
| 01 | 2017 | GESAMT | 2714 | Schleswig-Holstein | |
| 02 | 2017 | GESAMT | 5608 | Hamburg | |
| 03 | 2017 | GESAMT | 8785 | Niedersachsen |
How to use dg_call
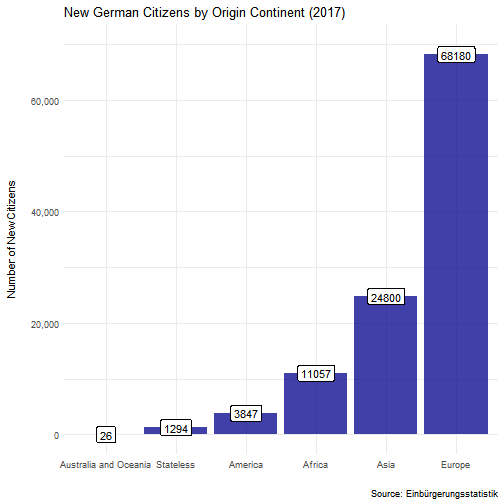
dg_call(nuts_nr = 1, # NUTS-1 year = 2017, # Specify Year stat_name = "BEV008", # Stats on New Citizens substat_name = "STAKNW") %>% # By Continent filter(STAKNW != "GESAMT") %>% group_by(param_description_en) %>% summarise(value = sum(value)) %>% mutate(param_description_en = ifelse(str_detect(param_description_en, "Stateless"), "Stateless", param_description_en)) %>% mutate(param_description_en = fct_reorder(param_description_en, value)) %>% ggplot(aes(param_description_en, value)) + geom_col(fill = "darkblue", alpha = .75) + geom_label(aes(label = value)) + theme_minimal() + labs(x = "", y = "Number of New Citizens\n", title = "New German Citizens by Origin Continent (2017)", caption = "Source: Einbürgerungsstatistik") + scale_y_continuous(labels = scales::comma, limits = c(0, 70000))How to use dg_call
How to use dg_map
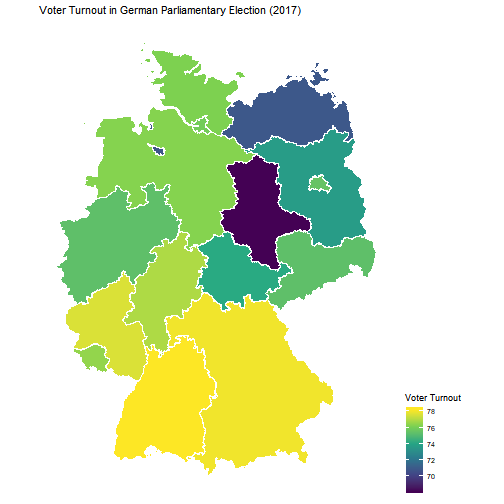
dg_map(nuts_nr = 1, year = 2017, stat_name = "AI0506") + ggthemes::theme_map() + ggplot2::scale_fill_viridis_c("Voter Turnout") + ggplot2::ggtitle("Voter Turnout in German Parliamentary Election (2017)") + ggplot2::theme(legend.position = "right")How to use dg_map
More Maps!

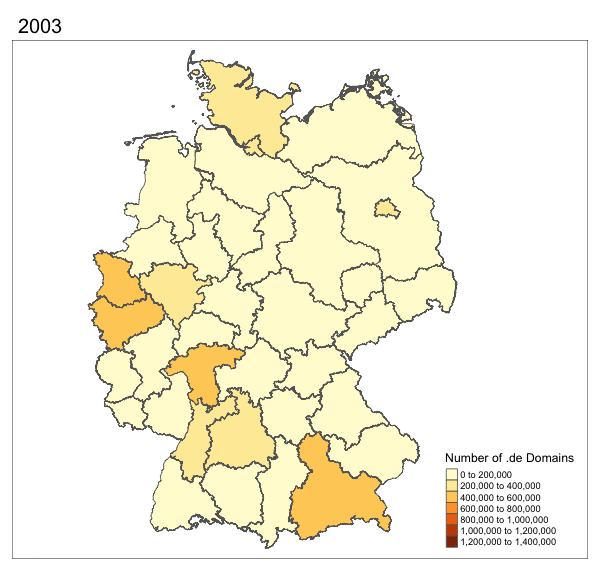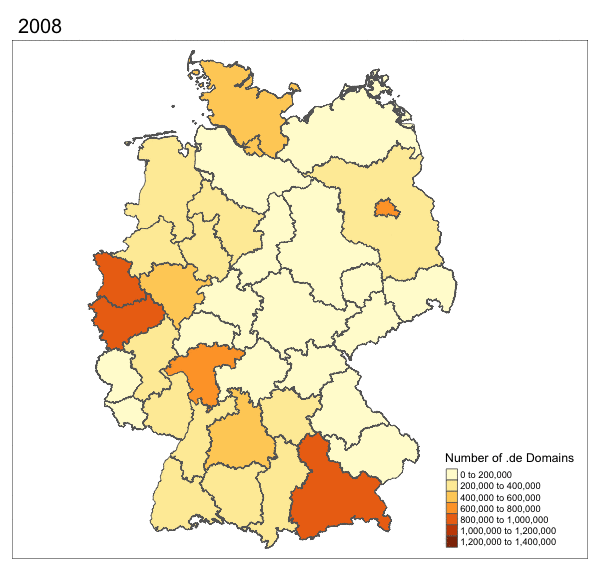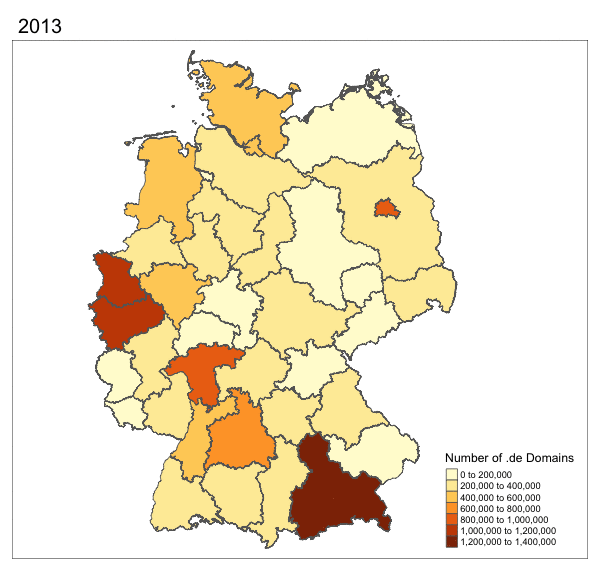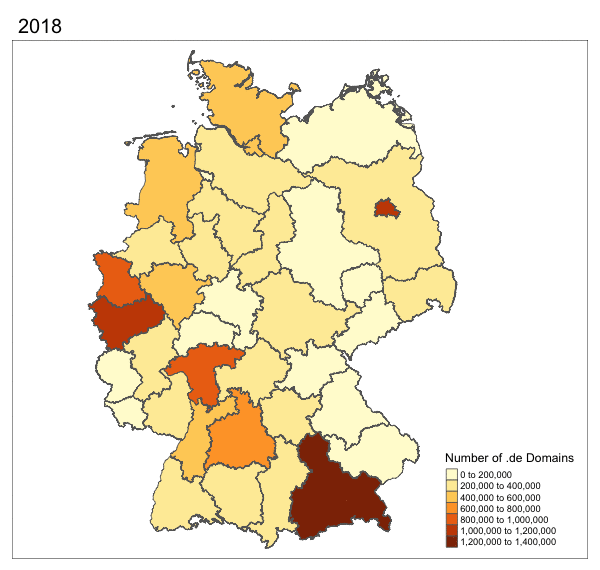
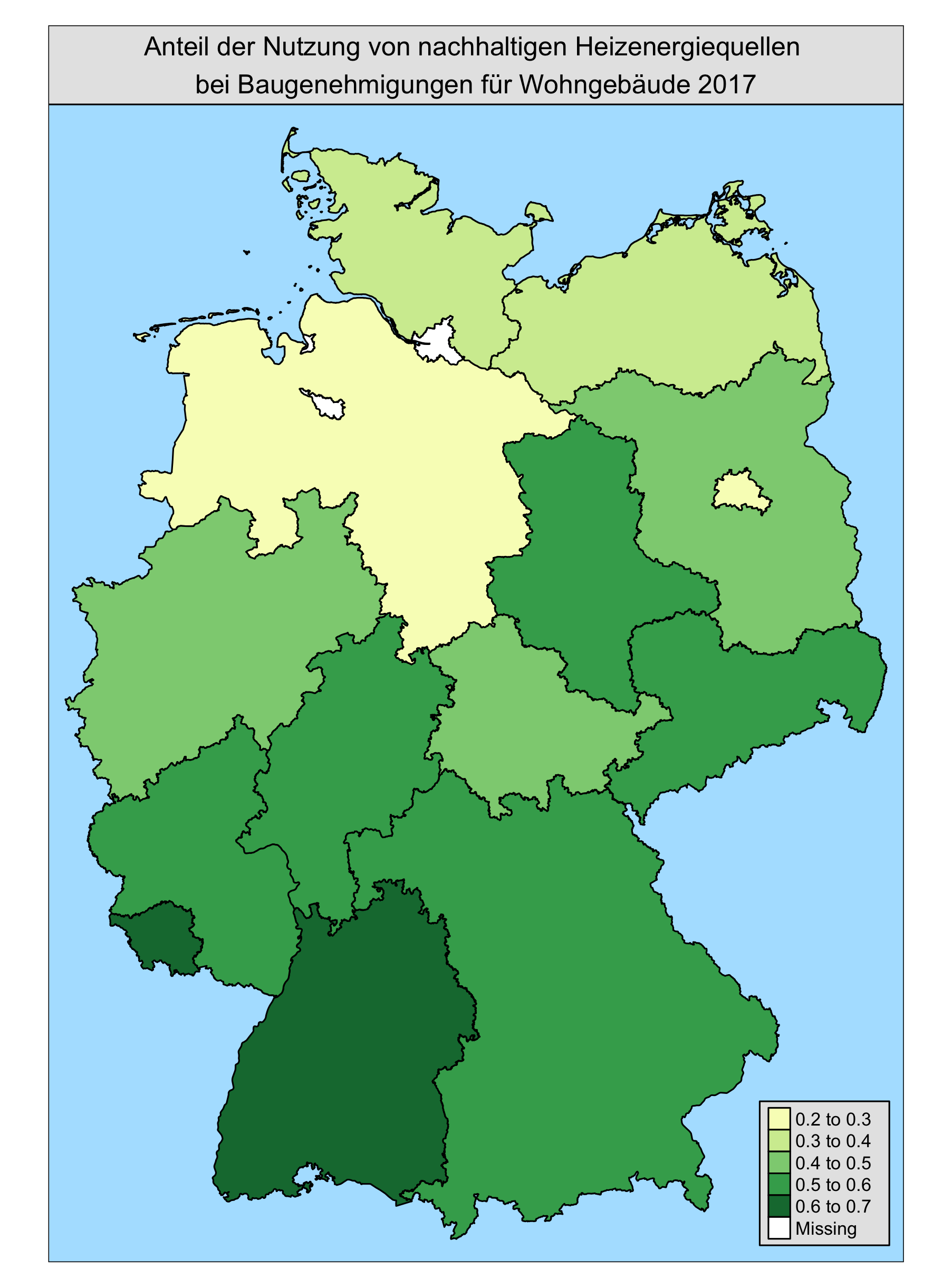
Hackathon Instructions
- Material
- You can fork/download this GitHub repository, which includes the slides and some example code.
- You can also use Rstudio Cloud. We set up a "workspace" with all necessary packages pre-installed. Here is the invite link.
- If you are looking for use cases of
datenguideRcheck out the folder/scripts.
In the end, you can present your dashboards, shiny apps, plots or analyses.
The best submissions will be shared on Twitter (if they want to of course!:)
Important:
If you encounter any bugs, please use our issue tracker on GitHub.
Some Examples and Challenges
| stat_name | description_en | challenge |
|---|---|---|
| AENW01 | Disposed / Treated Amount of Waste A.d. Own BL | Environmental Protection / Sustainability |
| AI1901 | Household Waste per Inhabitant | Environmental Protection / Sustainability |
| AI_Z04 | Share of Persons with MHG in the Total Population | Migration |
| AI0801 | Unemployment Rate | Unemployment |
| AI2102 | SGB II Quota Up to 64 Years | Unemployment |
| ERW009 | Unemployment Rate on all Acquisition Persons. | Unemployment |
| AI0506 | Voter Turnout, Federal Election | Politics |
| AI0606 | Voter Turnout, European Elections | Politics |
| WAHL09 | Valid Second Votes | Politics |
| WAHLSR | Voter Turnout | Politics |
| AI1302 | Road Traffic Accidents per 10,000 Inhabitants | Traffic |
| AI1304 | Fatalities in Road Traffic Accidents per 100,000 Inhabitants | Traffic |
| AI1601 | Disposable Income per Inhabitant | Social Inequality |
| AI1703 | GDP per Inhabitant | Social Inequality |
| FLC001 | Living Space in Residential Buildings | Housing |
| BAU009 | Residential Building | Housing |
| WOHNGB | Residential Building | Housing |
It's time to type some R code

Let's get to the
H A C K I N G
Thank you for listening